With 1.2 million deaths in 2020, accounting for 23% of the total deaths, cancer is the most important disease. 2nd biggest killer in the European Union. This number is even more tragic when you consider that 40% of these cancers are preventable by: Early detection and lifestyle improvement Things like quitting smoking and regular exercise.
However, research into the future of medicine offers hope, with major advances in disease prevention and treatment predicted to occur in the coming decades. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI), in particular, is one major cause for optimism.
What exactly does AI in healthcare involve?
many recent research papers Show that AI has the potential to: Transforming healthcare Delivering new ways to improve cancer prevention, diagnosis, treatment and management across many therapeutic areas (particularly oncology, cardiology and ophthalmology) and across the entire value chain, from research, development and production to marketing By that. Overall, patients receive better treatment.
Looking at the market numbers, the growth of AI in healthcare is evident in the number of players. Aside from the rise of AI startups, 18 out of 47 multinational AI companies currently offer services. healthcare solutions. Of these, 80% provide innovative treatment-specific solutions, and 20% develop efficiency-based tools to optimize resources and hone medical technology.
AI will contribute to 6 areas in particular:
-
medical research: AI can accelerate the development of new treatments by analyzing large amounts of data to identify promising compounds and predict their efficacy. This technology is expected to speed up clinical research by identifying patients for clinical trials and have a major impact on drug development. Analyze the data generated by these tests
-
medical diagnosis: AI helps doctors make faster and more accurate diagnoses by analyzing medical data, such as X-ray images, test results, and specific medical history. AI algorithms can detect early signs of disease and help identify the most appropriate treatment. Among many other examples, Breast Cancer of Wisconsin used specific machine learning algorithms and applied them to breast cancer diagnosis with the following results: 98.53% classification accuracy.
-
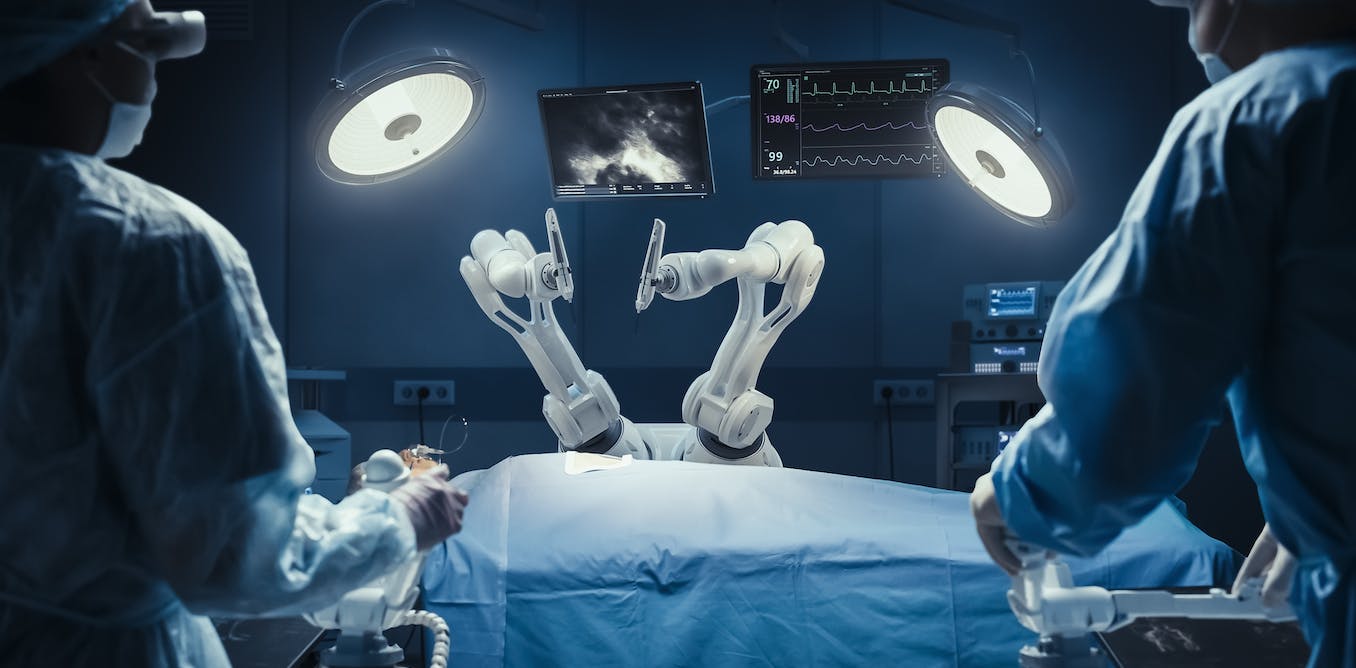
Surgical assistance: AI helps surgeons plan and perform complex surgical procedures, including preoperative planning, intraoperative approaches, and predicting postoperative complications. AI-assisted surgical robots provide greater precision and Patients recover faster after surgery.
-
patient monitoring: AI can be used to monitor a patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels, and alert healthcare professionals if any abnormalities occur. This is predicted to be a game-changer for patients with chronic diseases, allowing for thorough monitoring and early intervention if complications arise.
-
individual treatment: AI can take into account vast amounts of medical data to determine the most targeted treatment for a patient, taking into account the patient’s genetic profile, medical history, lifestyle, and many other specific characteristics.
-
medical record management: AI can automate electronic medical record management, making it more efficient and accurate while ensuring the confidentiality and security of patient information.
Diagnostic announcement procedure
Among the sectors outlined above, the AI-assisted medical diagnostics market is performing particularly well.Currently worth $1.3 billion, with annual growth expected to exceed $10 billion 23% over the next five years, reaching $3.7 billion in 2028. Cloud-based medical image analysis software in particular is already in high demand. Fields such as mammography, CT scan, MRI, etc. Benefit from technology first.
In reality, however, many hospitals suffer from a lack of technological resources, making it difficult to harness the potential of AI. Consider pathology slides based on analysis of biological abnormalities. Training AI models requires digitizing all slides, but the majority of European institutions currently do not have the equipment to do so.
Treatment management, support and post-treatment monitoring
AI can be used at every stage of cancer treatment, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on higher-value tasks such as direct patient care, psychological support, critical technical decisions, and clinical trials. . This can lead to improved patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare systems.
Three areas of particular importance benefit from technology:
- Organization management toolsThis saves doctors a lot of time in their daily tasks. Some of these can help monitor patient flow, reduce administrative burden, and record notes to complete medical records thanks to automated transcription software.
–Predictive analysis tools, collect and analyze large amounts of patient data to determine which health category the patient belongs to. This allows for more personalized and efficient treatment.
-
Surgery support tools using AI, based on medical robotics. These techniques are still frequently used for simple surgical procedures such as suturing.
-
remote monitoring Using digital medical devices, medical professionals can remotely interpret patient health data collected at home and make treatment decisions. Remote monitoring systems aim to improve patient health through regular monitoring.
-
chatbot It can also be integrated into a wide range of applications (Messenger, Slack). These can be used throughout the entire patient care process, but are especially useful during ongoing monitoring periods. Support is vital.
Limitations of AI in healthcare
Despite all these exciting prospects, a series of challenges must be overcome to reap the full benefits of AI-assisted medicine.
First, AI is not yet sophisticated from a technical perspective. For example, there is currently no universal format for data health, making it difficult to clean and transfer data from one software or computer to another. Most AI solutions also require human training rather than humans. Engineers will need to work with medical experts to listen carefully to the needs of the medical community and reflect them in new AI.
It is well known that sociocultural and ethical issues also need to be considered. Even though the European Union’s 2018 data processing framework regulation, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), gave individuals the power to decide how companies treat their personal information, data protection remains This is a real problem for many people.of EU AI lawthe world’s first comprehensive law regulating AI machines that pose risks to health, human rights, and safety, should also go some way to alleviating these concerns.
This article was co-authored with Rym Aouchiche, a former student of Professor Frédéric Jallat and currently working as a Life Sciences and Strategy Associate Consultant at IQVIA.